In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into business operations has shifted from experimental to essential, transforming industries and reshaping the way companies function. As more businesses adopt AI technologies, the impact is profound—touching everything from cost management to customer engagement, operational efficiency, and revenue generation.
This article explores the significant effects of AI on business performance and organizational functions, drawing key insights from the latest findings in the 2024 AI Index Report.
The Impact of AI on Business Performance
Cost Reduction
One of the primary benefits of adopting AI in business is a substantial reduction in operational costs. According to McKinsey’s 2023 survey, as cited in the AI Index Report, industries such as manufacturing, service operations, and risk management have seen significant cost savings. Notably, 55% of respondents in the manufacturing sector reported cost reductions, highlighting AI’s role in optimizing production and minimizing waste.
Revenue Growth
AI doesn’t just help cut costs—it also drives revenue. The same McKinsey survey showed notable revenue increases across various sectors, particularly in manufacturing, marketing, and sales, with 66% and 65% of companies in these fields reporting gains, respectively. This growth is largely attributed to AI’s ability to enhance decision-making, personalize marketing efforts, and streamline sales processes.
Improved Business Efficiency
Overall, the survey revealed that 42% of organizations have reduced costs through AI, while 59% reported increased revenue. These figures reflect a dynamic shift in how businesses perceive and deploy AI—not just as a cost-cutting tool, but as a fundamental driver of profit maximization.
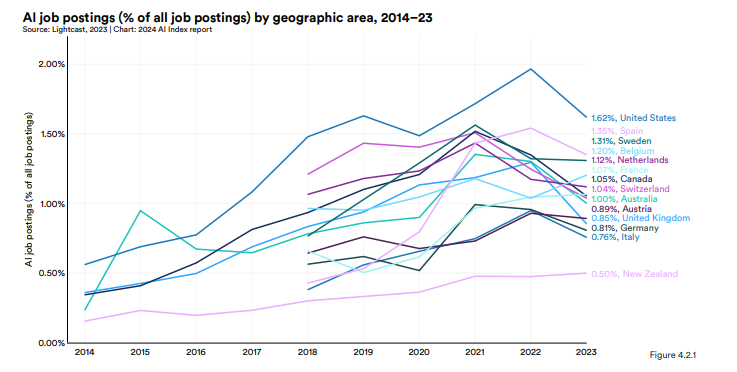
(Chart: Percentage of job postings requiring AI skills)
AI Adoption Across Organizational Functions
Widespread Implementation
The 2024 AI Index Report shows a growing trend in AI adoption, with 55% of organizations now using AI in at least one business function—a significant jump from just 20% in 2017. This increase underscores rising confidence in and reliance on AI technologies across various business domains.
Regional and Functional Variations
Europe leads in AI adoption, while other regions also demonstrate strong growth. AI is being used across a range of applications, including service operations optimization, enhanced personalization, customer engagement, and AI-driven product improvement. The most common uses of AI are in service operations (26%), personalization (23%), customer engagement (22%), and product enhancement based on AI insights (22%). These functions highlight the diverse and expanding applications of AI across business sectors.
The Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI—a subset of AI technology—is gaining traction for its ability to automate complex and creative tasks such as drafting documents, generating personalized marketing messages, and summarizing lengthy texts. Its growing adoption underscores AI’s potential to handle tasks that have traditionally required significant human creativity and intellectual input.

(Chart: Growth rate of job opportunities related to Generative AI)
Conclusion
The integration of AI into business operations is no longer a future concept—it’s a present-day reality with tangible impacts. Its effectiveness in cost management and revenue generation is reshaping traditional business models and operational strategies. As AI technology continues to advance, its role in driving business innovation and competitive advantage will only expand, making AI adoption not just beneficial but essential for future-ready enterprises.
In summary, as businesses continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, AI’s role as a catalyst for innovation and growth remains clear. Insights from the 2024 AI Index Report not only reinforce the importance of AI in modern business practices but also highlight the strategic need to fully leverage its potential.
Source: aiindex.stanford.edu


